Geo blocking video (or geo-restriction) is the practice of restricting access to online video content based on a user’s geographic location. If you’ve ever seen the message “This video is not available in your country,” you’ve encountered geo blocking. Content providers use this technique to control where their videos can be viewed, often to comply with licensing agreements, local laws, or business strategies. In this updated 2025 guide, we understand into why geo-blocking matters, how it works (covering IP-based, GPS-based, and DNS-based methods), tools and services to implement it, how to tackle VPNs and proxies in video streaming.
Table Of Content:
Video-sharing services and streaming platforms, like YouTube, Netflix, and Hulu, use geo-restrictions to make some of their content inaccessible to users from specific regions. This means that people in certain countries or regions are prevented from accessing certain websites or online services. The geo-restrictions practice holds great value for companies, especially ones with large amounts of intellectual property accessible online. Overall, geo-blocking is a powerful tool that can be used for various purposes. It is important to understand how it works and how it can be used to make the most of its potential.
VdoCipher helps ver 3000+ customers over 120+ countries to host their videos securely, helping them to boost their video revenues.
Geo-blocking restricts access to an online service based on the users’ geographic location. When a user tries to access a website or online content restricted by IP based geo-blocking, the website will check the user’s IP address. If the IP address is not in the database of allowed locations, the user will be blocked from accessing the content.
How Geo-Blocking works
At its core, geo-blocking works by determining the user’s location and then allowing or denying access based on that location. The most common mechanism is IP address detection, but there are other techniques as well. Here’s a breakdown of how geo-blocking is implemented:
IP Address Geolocation
Each computer and digital device on the internet has a unique IP (Internet Protocol) numerical identifier known as IP Address. Every IP address has four octets, each of which can be between 1 and 256, separated by periods. IP addresses are necessary for Internet communication because they allow computers to recognize and connect. Whenever your computer (or device) requests to access content on a server, the server knows where to send the content based on your IP address. Depending on whether or not the server is allowed to display the requested content to IP addresses from specific geographical regions, it will either respond with the requested data or not do it and redirect you to a different page.
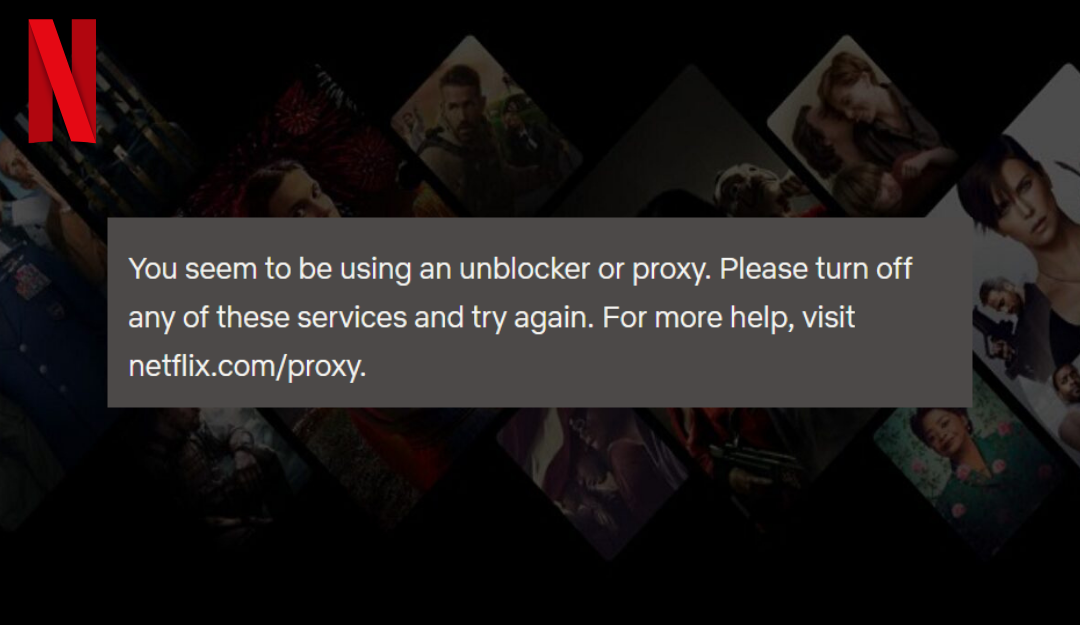
Geo-restrictions can be seen in a blocked website, streaming service or even a particular piece of content unavailability, such as a Hulu video. You must have seen Geo-blocking when you pay for a premium service like Netflix or Hulu. For example, if you live in the US and have an active Netflix subscription, you can stream the content only when you are within the US geographical region. If you go on vacation or access your account from other countries, you will not be able to access your same Netflix library.
GPS-Based Location
In mobile apps or smart TV apps, services may also use GPS or other device location services for more precise positioning. This method requires user permission (to access their GPS coordinates). If granted, the app can get an exact latitude/longitude from the device’s GPS hardware. This is far more precise than IP, useful for scenarios like sports blackouts which might be enforced at a city or zip-code level. GPS-based geo-blocking can detect if a user is within a restricted zone even if their IP might suggest otherwise.
Alongside these geolocation technologies like Uniqode’s QR code tracking is increasingly used by content providers and marketers to offer location-based access or promotions. By scanning QR codes tagged to specific regions or events, users can gain streamlined access to geo-restricted content or localized offerings, while providers gain valuable data on user engagement and geographical reach.
For example, sports streaming apps (like ESPN+ or MLB.TV) often request your GPS location on mobile to ensure you’re not spoofing location; they cross-verify that your device’s GPS coordinates match the allowed region, not just your IP.
The downside is user experience – not all users will share location, and GPS only works on devices (not in a basic web browser without special APIs). It’s mostly a supplement to IP-based checks for high-stakes content like live sports.
DNS-Based Filtering
Some services implement geo-blocking at the DNS level or via DNS-based proxies. One approach is DNS filtering, where the service detects the geographic source of DNS requests for the video service’s domain and blocks or permits access accordingly.
For instance, if a DNS request for a video stream comes from a disallowed country, the DNS server might refuse to resolve the stream URL or direct it to a block message. Another context is Smart DNS services – these are user tools to bypass geoblocks by resolving DNS through an allowed region. Content providers counter this by detecting inconsistencies: e.g., Netflix famously checks for DNS-based circumvention by making the user’s app fetch content from multiple domains. If one request goes via a proxy and another directly, the IP mismatch flags a geo-bypass attempt.
In short, DNS-based geo-blocking is about controlling or verifying the network paths at the name resolution stage, often used in conjunction with IP checks for additional enforcement.
Application-Layer & Other Methods
Some platforms might enforce geo-restrictions in application logic (e.g., not showing certain videos in the catalog if your profile’s country is different). Others measure network characteristics. For example, checking end-to-end latency can sometimes help infer if a user is truly in a region (though this is not common and can be unreliable). In most cases, IP, GPS, and DNS cover the techniques in use. Cookies or account settings are rarely used for geo-blocking (since users could easily falsify those), but they might come into play for secondary checks or region-specific experiences.
| Method | Location Detection | Pros | Cons | Typical Use Case |
| IP-Based | Uses IP geolocation DBs | Easy to implement; no user input | Coarse accuracy; spoofable by VPNs |
Netflix region catalogs, BBC iPlayer
|
| GPS-Based | Device GPS (needs consent) | Highly accurate; hard to fake | Requires native app & user permission |
Mobile apps like ESPN+ for blackouts
|
| DNS-Based | Analyzes DNS requests | Catches Smart DNS; proxy defense | Technical setup; false positives |
Netflix detecting Smart DNS usage
|
Why is Geo Blocking Video & Digital Content Important?
There are several reasons why geo-blocking may be used. For example, a website may only want to provide services to users in a particular country to comply with local laws and regulations. Or, a website may only have the right to show specific content in certain countries. It is also used to block access to websites promoting illegal activities in some countries, such as online gambling. You may have seen online retailers, such as Amazon, using geo-blocking to make people use the local version of their website, which may charge higher prices than those listed in other countries.
Finally, geo-restrictions can also be used to control the spread of information. For example, a government might place a geo-restriction on a news website to prevent people from learning about a particular event. Geo-blocking can be frustrating for users who are prevented from accessing content that they want to see. However, it is important to remember that geo-blocking is a legal and legitimate way for website owners to control who can access their content. Whether or not geo-blocking is legal depends on the specific circumstances and jurisdiction.
In the bigger picture, geo-blocking is implied for
Licensing & Copyright Compliance – Movies, TV shows, and live sports are typically licensed on a country-by-country or region-by-region basis. Streaming platforms must enforce geo-restrictions to honor these contracts. Failing to do so could lead to legal consequences or loss of distribution rights. Geo-blocking ensures providers meet their contractual obligations and avoid costly lawsuits. In fact, geo blocking video is often legally necessary for platforms to respect exclusive territorial licensing deals.
Regional Regulations & Censorship – Different countries have varying laws about what content is permissible. In 2025, this is increasingly pertinent, from privacy regulations to censorship rules. For example, some governments mandate blocking certain content (news, political, or adult content) within their borders. Geo blocking allows services to comply with local laws by preventing access where content is illegal or culturally sensitive. It’s also used to enforce sanctions or block content in specific regions as required by law.
Market Segmentation & Content Strategy – Streaming services now routinely tailor content libraries and recommendations to regional audiences. Geo-blocking helps in market segmentation, letting platforms highlight region-specific titles and manage content rollouts. For instance, OTT providers might release a new film or series in one country before another and use geo-blocking to enforce staggered release schedules. It also enables variable pricing strategies, services can set different subscription or rental prices in different markets and ensure users only see the pricing intended for their location.
Revenue Protection & Demand Control – By controlling where content is available, content owners can maximize revenue. This includes tactics like regional exclusives and preventing audience “leakage” across borders. For example, a video game might be sold in North America first and later in Europe; geo-blocking prevents users from other regions accessing it prematurely. Similarly, sports leagues enforce local blackouts so that local broadcasters (who pay for exclusive rights) retain their viewership, a form of geo-blocking critical for live sports business models.
User Experience & Distribution Logistics – Sometimes geo-blocking is used to manage network load or direct users to the appropriate regional service. Large platforms (e.g., Amazon or Netflix) might redirect users to their country-specific site version. This ensures content is localized (language, subtitles) and that users get a better experience suited to their region. In some cases, companies even use geo-blocking to comply with data laws. For instance, avoiding serving users in regions where they cannot meet data protection rules.
Despite some consumer frustration, geo-blocking remains vital in 2025 for balancing global reach with local requirements. With the explosion of VPN usage (over 40% of internet users have used a VPN to access geo-blocked content, content providers are doubling down on geo-blocking to protect their interests. In the next sections, we’ll explore concrete use cases, how geo-blocking is implemented technically, and how services are staying ahead of VPNs and other circumvention tools.
To geo-block, a website may choose to block the network connection entirely, resulting in timeouts when trying to access the site. Other websites might serve a custom block page explaining why access is denied. Geo-restrictions may also happen at the application layer. A user may be able to load a site’s main page but find that the login button has disappeared or that some content is not available.
How is geo-block implemented?
There are a few different ways that geo-blocking can be implemented. The most common is to use IP addresses to determine a user’s location. IP addresses are assigned to internet-connected devices and can be used to approximate a user’s geographic location.
Another way to geo-block content is to use website cookies. Cookies are small pieces of data stored on a user’s computer and can be used to track their web browsing activity. By setting a cookie, a website can restrict access to users who are not in the desired geographic location.
Finally, some websites use geolocation services to determine a user’s location. These services use information like GPS data, IP addresses, and WiFi networks to triangulate a user’s position.
Geo-blocking is a controversial practice and has been the subject of several lawsuits. In some cases, geo-blocking is used to comply with copyright and licensing restrictions. In others, it may be used to discriminate against certain users or regions unfairly.
If you’re looking to access geo-blocked content in your country, there are a few ways to get around it. Using a VPN or proxy server can change your IP address and trick websites into thinking you’re in a different location. Additionally, some web browsers allow you to change your geographic location. You can prefer guides when choosing the best residential proxy, as some of them offer real IPs from real devices with the backing of real ISPs, which can prevent any restriction and ensure a more seamless online experience.
Common ways of blocking video access to avoid infringing copyrights
Blacklisting popular VPN providers – A VPN provider is a company that provides virtual private networking (VPN) services. VPN providers use various technologies to create a secure connection between a user’s computer and the company’s network. There are a few popular ways that VPN providers bypass geo-blocking. One way is to use a server located in a country that is not subject to geoblocking. Another way is to use a VPN provider that uses “stealth mode.” Technology. Stealth mode protocol (OpenVPN) is a technology that makes it difficult for ISPs to detect that a VPN is being used. Modern VPN detection also use behavioral clues, algorithms analyze traffic for patterns (e.g., rapid IP switching, or an IP that claims to be residential but has datacenter-like traffic patterns). Some providers perform real-time protocol scanning on connections to see if they match VPN protocols. Video streaming platforms like Netflix use industry-standard technologies to blacklist popular VPNs.
Blocking connections from the same IP range – Users accessing a website or streaming platform from the same VPN server will have IPs within the same range. Blocking connections from the same IP range is a security measure to secure a connection between a particular IP or group of IP addresses. It is usually done to block or ban any undesirable hosts or websites from entering the node or server. This way, it ensures users access only the content available to their geolocation.
Explore More ✅
Protect Your VOD & OTT Platform With VdoCipher Multi-DRM Support
VdoCipher helps several VOD and OTT Platforms to host their videos securely, helping them to boost their video revenues.
Blacklisting DNS unblockers – DNS unblocking services redirect you to a region where you can access a website with restrictions. For example, the DNS unblocking service will first send the traffic to a US located server when accessing Netflix from abroad. That US server with a US IP address will access Netflix on your behalf and make the content available. Netflix makes your device ping another domain, and if a different IP shows up, their system would know you are bypassing their geo-blocks.
The countermeasure is to blacklist known Smart DNS service IPs and to perform consistency checks (ensuring all requests for a session come from the same region/IP). Many Smart DNS users have found these tricks less effective as streaming services tightened these defenses.
Traffic Pattern and AI Detection – Advanced services in 2025 employ AI to detect VPN/proxy usage beyond simple IP lists. For instance, AI models analyze traffic timing, volume, and distribution. A legitimate home user tends to use one relatively stable IP and have a “human” usage pattern, whereas a VPN exit might handle many different streams rapidly. Machine learning can identify subtle differences, such as an IP that shows impossibly diverse geographic access in a short span. AI can also correlate data points like device fingerprint, time of day usage, and past history to assign an IP risk score. An IP that scores high (e.g., known datacenter + inconsistent behavior) can be blocked or at least challenged (maybe requiring a CAPTCHA or re-login).
| Method | How Users Bypass Geo-blocks | Platform Defenses |
| VPN Services | Tunnel traffic via foreign server to appear in allowed region |
Block VPN IPs, detect shared IPs, flag frequent IP switching
|
| Proxy / Tor | Use proxy or Tor exit nodes in target region |
Block known IPs, fingerprint traffic, restrict by region
|
| Smart DNS | Change DNS to redirect to allowed region |
Block known DNS proxies, test DNS consistency, use alternate fetch domains
|
| Residential Proxies | Route via real-user IPs, mimicking normal traffic |
Use behavioral analytics, flag abnormal patterns, restrict multi-region logins, partner with proxy detection tools
|
Geo-Blocking Video via VdoCipher
In the earlier part of the blog, we have seen why you don’t want certain digital assets to be globally accessible. You want restrictive access to videos, images and even documents based on geographical locations. Geoblocking is the way to do that.
VdoCipher, a secure DRM encrypted video hosting platform and a technical partner to AWS offers geo, IP and time-based restrictions to secure your videos. Vdocipher provides Hollywood grade DRM encryption similar to once used by Netflix and other streaming platforms. Video streamed via VdoCipher cannot be illegally downloaded using any software or internet plugins. Catering packaged video streaming solutions to e-learning, media and other marketing businesses, VdoCipher is helping them stream content on their site/app in a most secure and smooth manner.
Coming to IP Geo-restrictions on videos, VdoCipher has an easy to use Dashboard interface for implementing IP based Geo-restrictions. You can easily configure any complicated IP and country restrictions setting using the VdoCipher API guide. These restrictions can easily safeguard your videos on college and corporate networks. There are various code combinations used to create custom restrictions. If there is any confusion, do drop us a mail, and we can provide sample codes.
Subnet restriction is a security measure that allows an administrator to specify which subnets are allowed to access a network resource. This can be useful in preventing unauthorized access to a network or isolating a network from potential attacks.
IP Whitelisting & Blacklisting for Geo-Blocking
VdoCipher’s IP and Geo restriction uses JSON based configuration, allowing infinite customizability. For example, you may require a whitelist within a blacklist within a whitelist. It can be achieved with a small JSON in our config. The best part is the possibility of infinite nesting.
The IP whitelist allows for CIDR based configuration setup over corporate and university subnets. The CIDR configuration also allows you to constrain specific ISP networks. It proves valuable in setting up Value-added-services on ISP and Telecom networks.
Country-specific restriction sample code for playback access in only India and Great Britain:
[{
"action": "false",
"ipSet": [],
"countrySet": []
},
{
"action": "true",
"ipSet": [],
"countrySet": ["IN","GB"]
}]
Geo-Blocking is one of VdoCipher’s security features. Other multiple features for secure video hosting are:
- DRM Encrypted video streaming
- Dynamic watermarking to Block Screen Capture
- Offline downloads with time restrictions
- Smart HTML5 player with adaptive bitrate streaming
- Multi-DRM for videos (Google Widevine and Apple FairPlay)
- OTP-based backend authentication
- Ready-to-Use VdoCipher Plugin
Conclusion
Geo-blocking is often used to prevent users from accessing content not available in their country. For example, a user in the United States may be unable to access a website that is only available in the United Kingdom. Geo-blocking is a controversial practice, as it can be used to limit access to information and content. Critics argue that geo-blocking violates the free flow of information and creates artificial barriers to content.
Supporters of geo-blocking argue that it is necessary to protect intellectual property rights and prevent users from accessing content that is not intended for them. Geo-blocking has increased in recent years as more content is being made available online.
FAQs
What is meant by geo-blocking?
Geo-blocking is the process of restricting access to content based on a user’s geographic location. This can be done for a variety of reasons, including copyright protection, censorship, and security.
What is geo-blocked content?
Geo-blocked content is content that is only available in certain geographic locations. This can be due to copyright restrictions, censorship, or other reasons.

What is geo-restricted Netflix content?
Netflix content that is geo-restricted is content that is not available in all regions. This content is typically blocked due to licensing agreements that Netflix has in place with different content providers.
What are the consequences of geo-blocking?
There are a few potential consequences of geo-blocking. First, it can prevent people from accessing content that they would otherwise be able to enjoy. This can be frustrating for users, and may even lead to them finding ways to circumvent the geo-blocking (which can have legal consequences). Additionally, geo-blocking can also lead to decreased competition, as businesses in blocked regions may be at a disadvantage.
Supercharge Your Business with Videos
At VdoCipher we maintain the strongest content protection for videos. We also deliver the best viewer experience with brand friendly customisations. We'd love to hear from you, and help boost your video streaming business.


My expertise focuses on DRM encryption, CDN technologies, and streamlining marketing campaigns to drive engagement and growth. At VdoCipher, I’ve significantly enhanced digital experiences and contributed to in-depth technical discussions in the eLearning, Media, and Security sectors, showcasing a commitment to innovation and excellence in the digital landscape.