You’d have noticed that when you record or create a video, it is often of very high size. These files are called raw files, which are very large in size. These are further converted into relevant formats with the help of video codecs. This ensures that your video is compatible with all the different browsers and devices as they might support the different formats. One such video codec, which is being widely used is H.264 AVC.
H.264 Advanced Video Coding (AVC) is a well-known video codec. What exactly is it, and how does it work? How does it compare with other video encoders? Finally, what benefits does it offer? Read on, as we address each of these questions in detail.
TABLE OF CONTENT
An Introduction To H.264 Advanced Video Coding (AVC)
Before you understand what H.264 AVC is, you’d have to know about what is video encoding and what role video codecs play in this before we go on to describe H.264 AVC.
Why Do You Need A Video Encoder?
In the raw form, a video file takes up quite a bit of space. If a video streaming platform directly streams raw video files, then it will face challenges. The download might take a long time. There might be several lags and buffering while streaming video. Giving the viewer a very bad user experience.
This is why raw files are compressed to deal with these challenges. Video then takes up less space when you store it. You will find a smaller file much easier to transfer over the Internet and the streaming is also seamless.
The term “video encoding” refers to the process of compressing raw video files into a particular format for video streaming. This process also converts such video files into formats that are compatible with different browsers and devices.
Explore More ✅
Ensure Smooth & Secure Streaming of Your Videos With VdoCipher
VdoCipher helps 3000+ customers in over 180+ countries to host their videos securely, helping them to boost their video revenues.
What Is The Role Of Video Codec in Encoding?
This is where the term “codec” enters into this discussion. A video codec encodes a raw video file. You need a codec that offers both high video quality and a lower compressed bitrate. This would enable your viewers to watch high-quality videos on a wide range of video platforms.
A video codec compresses a raw video file so that it can be easily streamed online. It consists of an encoder and a decoder. An encoder compresses an analog video file, whereas a decoder decompresses the video file at the device to prepare the video for playback.
What video codec essentially does is that its encoder part first compresses the video file, and at the time of video playback, the decoder decompresses it for viewing.
Before H.264 AVC
When streaming a video, a video encoder converts the video into a compressed format. A decoder converts them back into a format that isn’t compressed.
Various manufacturers create hardware and software products to cater to the video streaming space. They can operate effectively only if the processes to encode and decode videos are standardized. While different manufactures can create their products differently, they will all need to follow the same standards. This improves interoperability.
Various standards for video encoding existed even before the advent of H.264 AVC. The following are a few examples:
- MPEG-2;
- H.263;
- MPEG-4 Part 2.
The quest for better video streaming quality along with lower video bitrates led industry stakeholders to develop H.264 AVC.
What is H.264 AVC?
H.264 or Advanced Video Coding is a video compression technique that is used widely to convert video to a format that takes up less space while transmitting or storing video files.
ITU-T (International Telecommunication Union) and ISO/IEC (International Organisation for Standardisation / International Electrotechnical Commission), two international standards bodies Created H.264. They published this video encoding standard in 2003 as part of a document named “Recommendation H.264: Advanced Video Coding”.
People often refer to H.264 as AVC (Advanced Video Coding). H.264 is also known as MPEG-4 Part 10. The above-mentioned standardization organizations don’t prescribe how manufacturers should implement video encoding. Manufacturers can decide that, however, they need to conform to the relevant standards.
H.264 AVC offers a higher quality of video and lower video bitrates than the earlier standards. It’s a widely used video encoding standard and is compatible with most devices available.
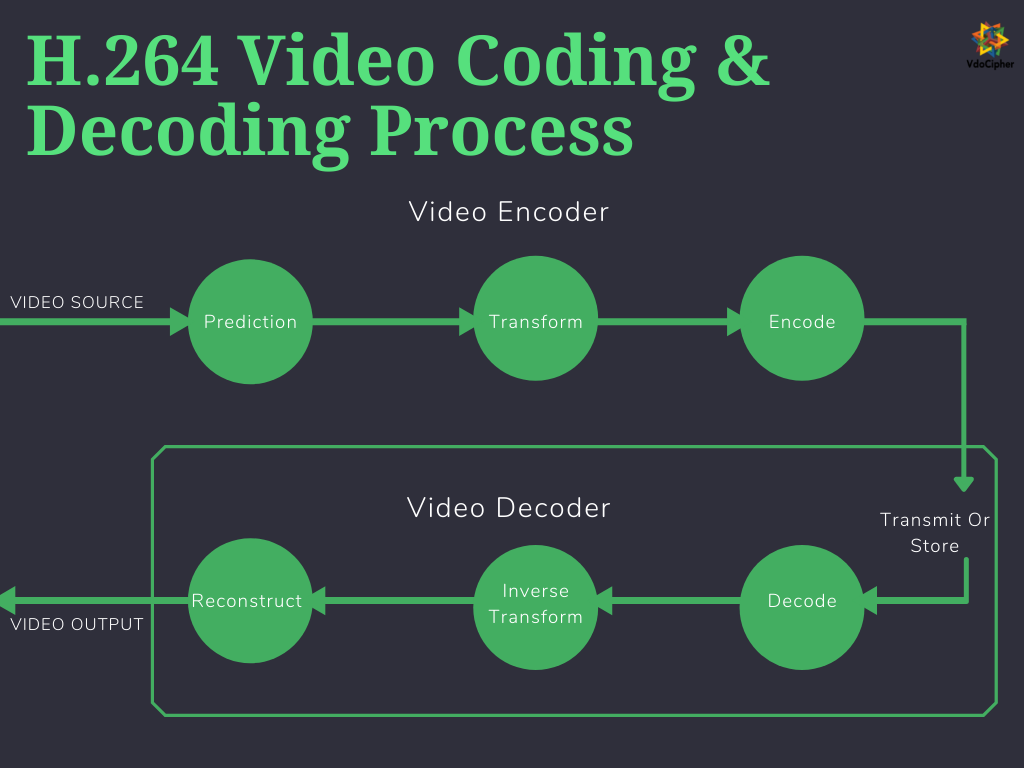
How Does H.264 AVC Work?
We now explain the working of H.264 AVC. This codec encodes a raw video, subsequently, it decodes it.
The processes involved in encoding videos
An H.264 codec performs the following processes to create a compressed H.264 bitstream:
- Prediction;
- Transformation and quantization;
- Encoding the bitstream.
1. Prediction
An H.264 video encoder uses a unit called “Macroblock” to process video frames. A macroblock refers to 16×16 displayed pixels.
The encoder creates a “prediction” of the macroblock. It might use previously encoded data from the current frame for this. That’s called “intra prediction”. Alternatively, the process might use data from frames that were coded and transmitted earlier. That’s called “inter prediction”.
The video encoder subtracts the prediction from the macroblock. The net result is called a “residual”.
Earlier video encoding standards had the prediction process too. However, H.264 AVC offers a more accurate prediction. That results in more efficient video compression.
2. Transformation and quantization
The transformation process uses “integer transform”, a mathematical algorithm to transform blocks of residual samples. The output of this process is a block of “transform coefficients”.
The subsequent process is called quantization. It uses mathematical algorithms too. The quantization process uses a parameter called the “quantization parameter” (QP).
A high value of QP results in high compression. The decoded image quality might degrade. On the other hand, a low value of QP results in a better quality of decoded images. The compression is lower in that case. Effective implementation of this codec requires striking a balance.
3. Encoding the bitstream
The above-mentioned processes create several data elements. A codec now needs to encode them to create a compresses bitstream. The key data elements are as follows:
- Quantized transform coefficients;
- The information that will help the decoder to re-create the prediction;
- The information about the structure of the compressed data;
- The information about the compression tools used for encoding;
- The information about the video sequence.
The encoding process uses mathematical algorithms like “variable-length coding” and “arithmetic coding” to create the compressed bitstream.
The processes involved in decoding videos
An H.264 codec performs the following processes to decode videos:
- Bitstream decoding;
- Reconstruction.
1. Bitstream decoding
This process includes the following steps:
- The video decoder receives the compressed bitstream.
- It decodes the syntax elements.
- The decoder extracts information like the quantized transform coefficients, prediction information, etc.
- It uses the above-mentioned information to reverse the coding process. This creates a sequence of video images.
- The decoder then “re-scales” the quantized transform coefficients. This step involves mathematical algorithms.
- The next step is called the “inverse transform”. This re-creates each block of residual data. It also combines these blocks, which creates a residual macroblock.
2. Reconstruction
The reconstruction process involves the following steps:
- The video decoder takes each macroblock, and it forms a prediction like the one created by the encoder.
- The next step involves adding the prediction to the decoded residual mentioned above. These steps create a decoded macroblock.
- Finally, the decoder displays it as a part of the video frame.
H.264 vs H.265: How Do They Differ?
H.265 is a new-generation video codec. ITU-T Video Coding Experts Group and ISO/IEC Moving Pictures Experts Group jointly created H.265. They released it in 2013. The H.265 video encoding standard is also known as High-Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC).
What H.265 does differently
H.265/HEVC bring the following key shifts in video encoding:
- It uses a different video encoding method than its predecessors like H.264. H.265 uses CTUs (Coding Tree Units) instead of macroblocks used by H.264. CTUs can have block structures that are 64×64 pixels.
- H.265/HVEC divides video images into different CTU sizes.
- CTUs with bigger pixel block size increases the coding efficiency of H.265.
These factors make H.265/HEVC a highly efficient video codec.
How does the H.264 vs H.265 comparison stack up?
We now compare H.264 vs H.265. The following differences are worth noting:
Technological advancements
H.265 is technologically more advanced than H.264. The following facts illustrate that:
- H.265/HEVC allows lower sizes of files for video streaming than H.264 AVC. Therefore, H.265 requires lower bandwidth.
- The H.265 codec uses CTUs. CTUs can process blocks up to 64×64 pixel. That surpasses macroblocks in H.264, which can process from 4×4 to 16×16. H.265 compresses video files more efficiently.
- H.265 offers better motion compensation and spatial prediction than H.264. This reduces the bandwidth and processing power requirements for users’ devices.
Supporting latest high-resolution imaging formats
H.264 handles SD and HD resolutions very well. The popularity of high-resolution imaging formats like 4K keeps growing, and H.264 has a limitation here. It creates a large file when storing 4K videos.
H265 does better here. It generates high-quality images. This codec also creates smaller video files. The H.264 vs H.265 comparison favors H.265 when it comes to handling high-resolution image formats.
Bandwidth and storage requirements
H.265 offers the video quality that’s offered by H.264, however, H.265 needs to manage less data. H.265 needs only half the bitrate needed by H.264. This reduces bandwidth and storage requirements. In turn, that reduces infrastructure costs. H.264 vs H.265 comparison favors H.265 here.
Popularity
H.264 AVC is well-established, however, H.265/HEVC is relatively new. More people are familiar with H.264. The H.264 vs H.265 comparison favors H.264 when it comes to popularity.
H.264 vs MPEG4 Comparison
As we mentioned, video encoding standards are evolving. MPEG4, also known as MPEG-4 is one of the predecessors of H.264. We now discuss how the H.264 vs MPEG4 comparison pan out.
A brief overview of MPEG4
The ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) created MPEG-4. This group released this video encoding standard in 1998. The following quick facts about MPEG-4 are noteworthy:
- The MPEG-4 standard deals with the compression of audio and visual digital data.
- This standard is still evolving. Remember that H.264 is also called “MPEG-4 Part 10”.
- MPEG4 offers better encoding efficiency than its predecessors like MPEG-2.
- MPEG4 has been used for compressing audio-visual (AV) data for the web. Voice applications like telephone and videophones use it, furthermore, broadcast television applications use this standard.
H.264 vs MPEG4 differences
The key H.264 vs MPEG4 differences are as follows:
Compression efficiency
H.264 uses newer technologies than MPEG-4. As far as the compression efficiency is concerned, H.264 is 1.5-2 times more efficient than MPEG-4. The H.264 vs MPEG4 comparison favors H.264 in this case.
Video quality
H.264 offers better video quality than MPEG-4. The former offers more fluent video playback than the latter. H.264 requires a lower bitrate than MPEG-4. H.264 clearly comes out better in the H.264 vs MPEG4 comparison.
Popularity
Both H.264 and MPEG-4 are established video encoding standards. They are compatible with nearly all devices and media players. However, H.264 is certainly more popular than MPEG-4.
The Advantages Of H.264 AVC
H.264 AVC offers several advantages. These are as follows:
Popularity
After its advent in 2003, H.264 AVC has become a well-established video encoding standard. All key devices and media players support this. A broad range of video streaming platforms supports this codec.
People working on the technical side of video streaming know this standard very well. Sufficient documentation exists on this codec. To sum up, the popularity of H.264 AVC makes it easy for broadcasters and developers of video streaming apps.
Performance
H.264 AVC offers significantly better performance than the earlier video encoding standards. Its compression efficiency is higher than the earlier standards.
This improved performance manifests in two different ways. These are as follows:
- H.264 AVC offers a better video quality at the same compressed bitrate.
- If you keep the video quality constant, then H.264 AVC offers a significantly lower compressed bitrate. That improves the video streaming experience.
Note: The higher performance of H.264 AVC is the result of technical sophistication. This codec involves more computational workload. That requires more processing power. You could argue that the increased requirement of processing power is a constraint. However, there’s increasing availability of media platforms and devices with more processing power. That eliminates the constraint. In fact, a more sophisticated codec like H.265/HVEC is gaining popularity!
Versatility
H.264 AVC offers considerable flexibility. It supports a range of compression options and transmission protocols. This codec works for low-bitrate mobile transmission as well as high definition consumer TV.
This video encoding standard includes the following:
- Integrated support for transmission and storage;
- Packetized compressed format;
- Capabilities to minimize transmission errors.
One can use H.264 AVC in a wide range of applications, e.g.:
- Online Video Streaming
- HD DVDs and Blu-Ray formats;
- HD TV broadcasting;
- Applications for Apple platforms, e.g., iTunes video downloads;
- Mobile TV broadcasting;
- Videoconferencing;
All In All
Multiple video encoding standards exist, and H.264 AVC is an important one among them. This standard represents key improvements from its predecessors. We reviewed how it works. We compared it with one well-known predecessor and a popular successor. Finally, we reviewed the advantages of H.264 AVC. Choose a video encoding standard according to your requirements.
Supercharge Your Business with Videos
At VdoCipher we maintain the strongest content protection for videos. We also deliver the best viewer experience with brand friendly customisations. We'd love to hear from you, and help boost your video streaming business.

Rahul Rana is Head of Marketing at VdoCipher Media Solutions, where he educates users about video streaming and media technologies. He writes about video streaming, live delivery, DRM, and building custom video players to help developers and teams learn practical techniques. Rahul enjoys breaking down complex media tech into clear, easy-to-understand guides and insights.