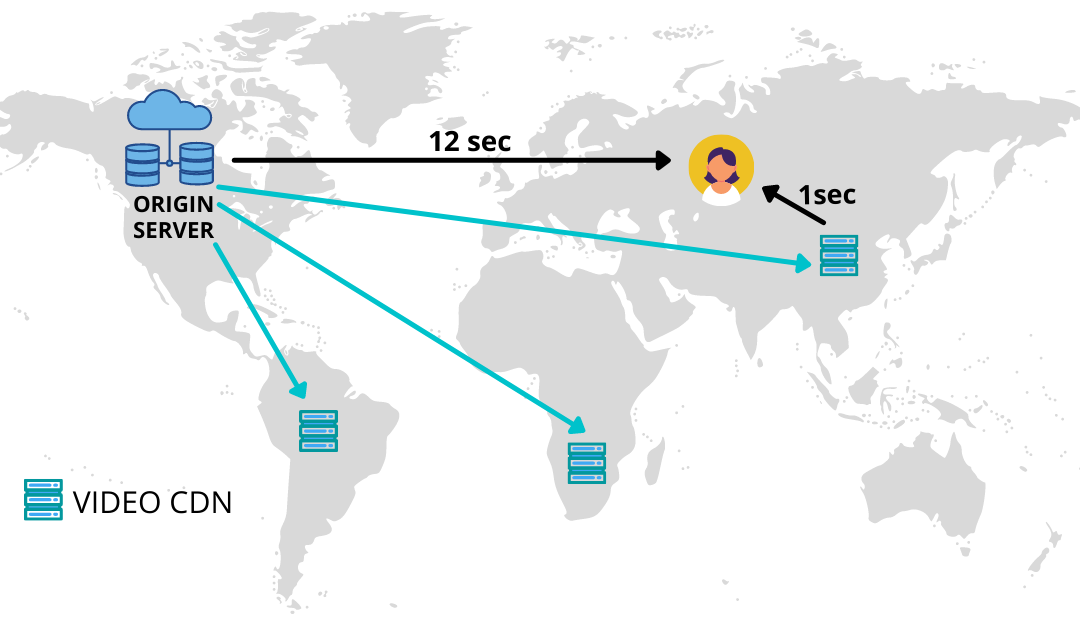
Let’s say John is in New Delhi, India, and wants to stream video content hosted on a website. The website is on a hosted server in California. When another viewer, Anne, who stays 500 km away from California, visits the website, the content loads pretty faster. But for John, who stays 12500 km away, the site takes comparatively more time to load as the website content has to travel more. This is where Video CDN comes to the rescue. The CDN finds an optimal server in physical locations closer to the physical location of the user.
Table of Contents:
- What is Video CDN or Video Content Delivery Network?
- Understanding Video CDN terminologies through Analogies
- Why use Video CDN Streaming?
- Benefits of CDN in Video Streaming
- Video CDN Technology and object caching process
- Why Single CDN isn’t enough?
- Multi CDN Approach to improve content delivery
- Building a Multi CDN Architecture
- Role of AI in Enhancing Video CDN
- Impact of using a CDN vs not
- Netflix Video CDN case study
- Live Streaming on Video CDN
- Best Video CDN for Video Hosting
- FAQs
CDN distributes the content over its various servers across the globe. The media file remains cached or temporarily stored on that CDN for other user requests in the same geographical region. The next time when a user requests the same content, the video file is served from the CDN, minimizing buffering, latency, and overwhelmed request burdens on the origin server. CDNs have freed host origins from the burden of distributing every content to the visitor from the website. The content is uninterruptedly served via CDN even when the servers go down, or the network is congested.
What is Video CDN or Video Content Delivery Network?
The streaming and delivery of a video stream require a considerable amount of resource utilization. This is attributed to video quality, video resolution, and higher bitrates of video streams, requiring more information to reach the users. Owing to the high performance and speed of distributing content without disruption to end-users, most websites now serve video content through CDNs. A video CDN is specially designed to support the smooth delivery of VOD platform and OTT platform content. For example, Netflix, YouTube, Disney+, Amazon Prime, Dailymotion, they all use CDN. Most CDNs cache web content like web pages, CSS style sheets, images alongside video content.
VdoCipher helps several VOD and OTT Platforms to host their videos securely, helping them to stop losing their video revenues.
Some video CDNs are built exclusively for video streaming. One such example is Open Connect, Netflix’s own distributed network. Content Delivery Networks or geographically distributed servers sit between the origin servers and the video players or clients to deliver a smooth viewing experience. In simple terms Video CDN can be considered as on demand distribution of a video file from nearby distribution centers which stores a copy for fastest delivery.
Understanding Video CDN terminologies through Analogies
Let’s understand some key aspects of a Video CDN and liken them to everyday situations:
- Global Distribution Network – Like a Chain of Grocery Stores: Think of the internet as a large city and your VOD website as a central warehouse that distributes goods (video content). A CDN is like having multiple grocery stores (CDN servers) spread throughout the city (the world). When a customer (user) needs groceries (video content), they go to the nearest store (CDN server) rather than the central warehouse, reducing travel time and ensuring faster service.
- Caching – Library Book Reserves: Caching on a CDN is akin to how libraries work with popular books. Imagine a book that’s frequently checked out. Instead of ordering it from a central library every time, local branches keep copies on hand. Similarly, CDNs store copies of popular web content on local servers. When someone requests this content, it’s quickly delivered from the nearest server, rather than fetching it from the main server every time.
- Dynamic Content Delivery – Personalized Shopping Experience: Delivering dynamic content through a CDN is like a personalized shopping experience. Imagine walking into a store where the sales staff knows your preferences and quickly brings you items that suit your taste. CDNs do something similar for dynamic web content (like user-specific data or live updates), optimizing the route and maintaining secure connections to deliver this personalized content efficiently.
- Edge Computing – Local Decision Making: Modern CDNs are capable of edge computing, which is similar to having local managers in stores making decisions on the spot, rather than waiting for instructions from the central headquarters. This local decision-making speeds up the process and tailors the service to the immediate needs of the customers (users).
In essence, a CDN like Amazon CloudFront operates like a well-oiled, distributed network of resources, ensuring efficient, secure, and personalized delivery of web content to users around the globe, much like a network of local stores providing goods quickly, securely, and as per the local demands.
Why use Video CDN Streaming?
Let’s say someone made a video and uploaded it on a website or social video platform. The video became a sensation, and viewers from across the globe are requesting playback simultaneously. Or say a website hosting videos has high traffic and experiences surges at times. What will happen to the origin server when thousands of requests hit the website? Obviously, at some point, the server will struggle to cater to the bulk requests made at the same time. Some viewers may want to play the start of the video, while some may play the latter video segments.
Not only the origin server has the complete video file will get clogged up, but also the time it will take to cater to global demand will increase heavily. This is because of the difference in distance the origin and request. Although data travels at speed of time but such bulk requests from far away distance will start creating buffering zones. Some packets of video file get sent and there is a wait, and then the next one gets received. This latency is what the end user making a playback request will feel.
The end-user will face several playback problems like video buffering, latency, website crashing, poor video quality, etc. When video streaming platforms merge with CDNs, the video content gets delivered in an uninterrupted and smooth manner.
Benefits of CDN in Video Streaming
Minimizes Latency and Buffering time
Buffering time and latency are directly related to how close the video content is to the viewer. CDN improves the performance by delivering content from the nearest server irrespective of device, location, or network usage. As a result, the video renders quickly, reducing any delays and ensuring the user remains engaged.
Reduces load on the origin server
Serving content from the CDN servers reduces the origin server being overwhelmed with stream requests. In addition, CDNs act as load balancers and prevent traffic congestion by alternating the request flow from origin servers to CDN servers.
Website Security
Denial-of-service attacks (DDoS) and web-based attacks are becoming very common. It becomes challenging to distinguish bad traffic from genuine traffic to prevent attacks on websites and web applications. Advanced Content delivery networks mitigate a wide range of attacks, including DDoS, without affecting the delivery and content availability. CDNs act as virtual fencing guards outside the core network infrastructure.
Reduces Bandwidth costs
Deploying Video CDN reduces the website operating cost as most of the content is cached and served via CDN. The origin server does not have to serve the content again and again. Higher the data transfer, the higher the video bandwidth consumption and cost. Because the CDN works in front of the origin server, less content is transferred from the origin server, reducing bandwidth cost.
Static Vs Dynamic Video CDN Comparison
| Aspect | Static Video CDN | Dynamic Video CDN |
| Content Type | Pre-recorded, unchanging video files (e.g., VOD) |
Live or personalized video streams (e.g., live streaming)
|
| Caching | Easily cached across CDN servers |
Challenging to cache as content changes in real-time
|
| Best Use Case | Video-on-Demand (VOD), non-time-sensitive content |
Live streaming, personalized video ads
|
| Management Effort | Low management effort; cached once and reused |
Higher management effort due to real-time updates
|
| Example | Netflix streaming movies or YouTube pre-recorded videos |
Live sports events, video conferencing (Zoom or Twitch live streams)
|
Video CDN Technology and object caching process
When a user requests a stream, the video is not delivered to the user’s device as a continuous file. The stream is, in fact, broken up into many smaller segments and further into bits. These bits get transferred from an online server, collected as segments, and then the user’s video player puts the loaded segment in the correct order.
This happens at the front end where the playback is requested, but as we already discussed, the online server here needs to be a CDN located nearest to the user.
Similar to playback, when a stream gets uploaded to a cloud CDN, each Video file gets uploaded in a stream on bits. These bits get distributed and cached by the CDN servers in strategically chosen locations across the globe. When a user makes a streaming request, the CDN caches the video segments as soon as they arrive from the origin server. Next time for the same stream request, the CDN serves those segments from the cache. This is faster as the media files are cached close to the clients and mitigate data packet losses.
Some CDNs start making copies of the video file as soon as it gets uploaded on the network, and others wait for a request from the nearest location and then make a copy. Also, these locations are Internet exchange points (IXPs) which are primary locations where different Internet service providers connect in order to provide each other access to traffic originating on their different networks. Through these high-speed connections and highly interconnected locations, a Video CDN provider is able to reduce time and cost with high-speed data delivery.
Why Single CDN isn’t enough?
Relying on a single Content Delivery Network (CDN) to distribute content can leave businesses vulnerable to performance degradation, outages, and poor user experiences. Even top-tier CDNs experience issues such as bottlenecks or server failures, impacting end-users. However, adopting a multi-CDN strategy allows businesses to mitigate these risks by distributing traffic across multiple providers.
While a single CDN may provide reliable service, it is not infallible. Issues like server overloads, micro-outages, and performance bottlenecks can lead to a subpar experience for users, particularly when delivering high-quality video, pay-per-view, or live content. In contrast, a multi-CDN strategy ensures that if one CDN experiences issues, traffic can be dynamically rerouted to another, maintaining a seamless experience for users.
Multi CDN Approach to improve content delivery
Multi CDN approach involves using more than one CDN provider simultaneously. By utilizing the resources of multiple CDN providers, the content delivery enhances reliability, performance and delivery time. Even if one CDN provider encounters downtime or performance issue, the other CDN will ensure seamless operation. VdoCipher uses Multi-CDN providers (AWS+Google Cloud) to ensure uninterrupted and smooth playback across multiple devices and regions.
Key Benefits of a Multi-CDN Strategy
Improved Performance and Reliability – With multiple CDNs, businesses can ensure better content delivery across different regions. Each CDN has its strengths and performs optimally in specific markets. Multi-CDN strategies allow businesses to allocate traffic based on regional performance, enhancing the overall user experience.
Faster Global Reach – Using multiple CDNs enables faster expansion into new markets. A single CDN might excel in North America but struggle in Asia or Europe. With a multi-CDN setup, businesses can choose the best-performing CDN for each market, ensuring content reaches global users efficiently.
Cost Efficiency – The competition between CDN providers often results in better pricing and lower operational costs. Additionally, spreading traffic across several CDNs reduces the risk of large-scale outages that can cost businesses both financially and reputationally.
Enhanced End-User Experience – By reducing downtime, buffering, and slow loading times, businesses can offer a consistently high-quality user experience, essential in competitive markets like OTT (over-the-top) video streaming.
Building a Multi CDN Architecture
Creating a multi-CDN setup requires attention to several key elements
Workflow Continuity – Ensure the new CDN partners can integrate smoothly into your existing infrastructure. You may need to identify which elements of your workflow must remain the same and which can be adjusted to maximize efficiency.
Traffic Distribution Policies – Not all CDNs are equally effective across all regions. It’s crucial to define clear policies that allocate traffic based on CDN strengths in specific areas. Real-time monitoring tools can help adjust these policies dynamically based on current performance metrics.
Performance Measurement – Use third-party tools to measure CDN performance impartially. Metrics like latency, error rates, and bit rates will help determine which CDN is best suited for specific regions or times of day.
Traffic Distribution Tools – DNS-based traffic management and client-side telemetry are the two primary methods for distributing traffic across multiple CDNs. DNS-based tools are straightforward but can be limited in real-time responsiveness, whereas client-side telemetry offers more granular control and real-time data about user experience.
Multi-CDN Best Practices
Data-Driven Decision Making – Measure global and regional performance data to guide traffic distribution policies, ensuring optimal performance in all markets.
Real-Time Monitoring – Implement real-time reporting tools to adjust CDN traffic on the fly, based on performance metrics like latency and error codes.
Client-Side Telemetry – This advanced technique allows you to monitor end-user experience directly and make traffic adjustments accordingly, ensuring superior performance for all users.
Collaborate Closely with CDN Partners – Maintain a strong relationship with your CDN providers to ensure seamless integration and optimal performance.
A multi-CDN strategy is no longer just a good idea, it’s essential for businesses focused on delivering high-quality content in today’s competitive environment. By reducing the risks of relying on a single provider, companies can ensure better performance, lower costs, and improved user experiences.
Role of AI in Enhancing Video CDN
The role of AI and Machine Learning (ML) in enhancing Video Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) is significant. AI and ML, two closely related technologies, are playing pivotal roles in improving CDN performance and efficiency. CDNs, which cache data in strategically placed data centers globally, utilize AI and ML to make intelligent routing decisions for content delivery, thereby improving server response times. These technologies enable network operators to identify traffic patterns and respond proactively to traffic demands, ensuring improved content performance. ML algorithms, trained on network data, can effectively make real-time routing decisions, reducing the occurrence of issues like HTTP errors or cache miss rates. This approach helps in managing increasingly complex networks effectively, enhancing user experiences, and unlocking new revenue streams. AI and ML-backed CDNs promise better performance at a more affordable cost, leading to excitement among industry leaders about their potential to deliver superior network performance and content delivery.
Impact of using a CDN vs not
The impact of using a Content Delivery Network (CDN) on website performance can be significant, as demonstrated by various metrics from real-world tests:
WEB
- GTmetrix Tool Analysis: A website’s performance rating improved from a B (85%) to an A (100%) after implementing a CDN. The Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), which measures the time taken for the largest content element on the page to load, improved from 1.6 seconds to 0.381 seconds, making it at least four times faster.
- WebPageTest Tool Results: Testing from three different locations (Virginia, London, and Singapore) showed improvements in First Contentful Paint (FCP) and Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) across all locations. For instance, in London, the FCP improved by five times (from 1.585 seconds to 0.390 seconds) and LCP by three times (from 2.585 seconds to 0.751 seconds).
- UPTrends CDN Performance Check: This test focused on the total time to load a page before and after using a CDN from multiple global cities. The results showed dramatic improvements. For example, in New York, the loading time decreased from 386 milliseconds to 60 milliseconds, and in Toronto, it went from 590 milliseconds to 11 milliseconds. These results indicate significantly faster loading times globally with the use of a CDN.
Video
- LiteBreeze Case Study: By moving video storage to cloud storage and delivering video using a CDN, significant improvements were observed. These included enhanced streaming performance, increased storage capability, and reduced load on the application server. Additionally, by channeling uploads through the CDN and moving heavy tasks to background workers for asynchronous execution, both the speed and user experience were improved. The ability to handle higher traffic volumes was also enhanced by scaling horizontally.
- Study on Live Video Streaming: Research on live video streaming quality of service (QoS) suggests that high bandwidth is crucial for maintaining QoS. CDNs, by being positioned closer to the user area, reduce access time compared to scenarios without CDN usage. The study also compared popular live streaming formats like HLS (HTTP Live Streaming) and RTMP (Real Time Messaging Protocol) with and without CDN. It concluded that live video streaming with CDN exhibited better performance than without CDN.
- Disney Streaming Metrics: Disney Streaming emphasizes limited rebuffering, quick video start times, minimal playback failures, and consistent high-bit-rate experiences. Their approach involves using a range of metrics to track and improve CDN performance. These metrics help in assessing the reliability and consistency of CDN services across different geographic regions.
These statistics and case studies highlight the considerable benefits of using a CDN in enhancing website performance, especially in terms of loading times, which is crucial for user experience and SEO rankings.
Netflix Video CDN case study
The Netflix CDN (Content Delivery Network) and cloud architecture case study provides a comprehensive view of how the company has leveraged cloud services and developed its own CDN system to optimize content delivery globally. Here’s an updated overview:
- Migration to AWS: In early 2016, Netflix completed its migration to AWS (Amazon Web Services), marking a significant transition from relying on private servers to using cloud storage and computing. This shift was a clear indicator of the growing importance and reliance on cloud services for large-scale digital enterprises.
- Microserver Infrastructure: Netflix’s infrastructure is divided into multiple microservers. Each of these servers has a relatively lower capacity and is dedicated to managing a single aspect of the service. This setup allows for the independent operation of each service component, contributing to the robustness and efficiency of the overall system.
- Development of Netlix’s own OpenConnect CDN: As Netflix’s traffic and volume grew, third-party CDN providers couldn’t keep up with the demand. In response, Netflix designed its own CDN called OpenConnect. This system involves installing Netflix’s CDN appliances in data centers of local ISPs. OpenConnect uses algorithms to calculate local content popularity and intelligently distribute content, thereby maximizing offload efficiency and reducing upstream demand. This approach has significantly reduced buffer times for viewers and improved overall streaming quality.
This case study showcases Netflix’s strategic approach to technology infrastructure, emphasizing the importance of cloud services and the development of a proprietary CDN to maintain its position as a leading content provider on a global scale.
Live Streaming on Video CDN
In live streaming, video, audio or other media data gets streamed over the internet in real-time. The content in live streaming works without first being recorded and stored. There are five steps involved in live stream content creation and consumption by the end-user. The steps are video capture, segmentation, compression and encoding, content distribution and CDN caching, decoding and playback.
| Aspect | Push CDN | Pull CDN |
| How it Works | Content is pre-uploaded to CDN edge servers. |
Content is fetched from the origin when requested.
|
| Best for | Popular or static content (e.g., movies, TV shows). |
Dynamic or unpredictable demand (e.g., live streams).
|
| Latency | Low, as content is already cached at the edge. |
Higher on first request; faster for subsequent ones.
|
| Cost | Higher, due to pre-storage on edge servers. |
Lower for infrequent requests; higher for popular content.
|
| Storage Requirements | High, as content is stored at multiple edge locations. |
Lower, as content is cached only after it’s requested.
|
| Traffic Handling | Better for high traffic; content is pre-distributed. |
Suited for low to moderate traffic.
|
| Content Freshness | Requires manual updates across CDN nodes. |
Automatically pulls the latest version from the origin.
|
| Use Case Examples | Netflix for popular shows. |
YouTube for less popular videos.
|
In live streaming, CDN caches the video segments as they get created in real-time. These segments get uploaded and are saved as copy of the original live stream. This copy will get further copied to various CDN servers located across the world. Thereafter, the video stream gets served from the CDN cache, not the origin server. But is there a waiting time between the live stream being cached and its delivery? If CDN efficiently caches each video segment, it becomes closer to being live rather than streamed directly from the origin server. Being closer to the user, serving CDN from live stream cuts down the round-trip time (RTT) to and fro the origin server. Also, CDN reduces latency, buffering and origin server overloading.
VdoCipher helps 2000+ customers over 40+ countries to host their videos securely, helping them to boost their video revenues.
Also, if there is a disruption of user’s local network and the stream gets stuck, the user can resume quickly from nearest CDN server.
Want to learn more about the tech powering streaming CDNs? Explore our in-depth guide on how streaming works to understand the intricacies behind smooth, real-time video delivery.
Best Video CDN for Video Hosting
Akamai
Akamai Video CDN is the name given to the set of CDN products released by Akamai Technologies, which combine a group of CDN servers and CDN servers that can deliver video and media. Originally launched in the United States and Canada in the 1990s, the CDN products became available in other regions during the 2000s. Akamai was one of the oldest CDN providers of the market, with over 250K servers in 135 countries.
Akamai Adaptive Media Delivery offers a consistent, high-quality viewing experience and is optimized for Adaptive Bitrate (ABR) Streaming. Built on Akamai’s Intelligent Edge Platform, the solution delivers HTTP-based live and on-demand streaming media. Akamai Adaptive Media Delivery supports HLS, HDS, MSS, MPEG-DASH and CMAF music and video formats. The other Akamai media solutions include Media Services Live, NetStorage and Cloud Wrapper.
VdoCipher Video CDN
With AWS-powered servers, Video DRM & CloudFront CDN infrastructure Vdocipher ensures video piracy protection with smooth video playback across 6 continents. Such an infrastructure can securely deliver your video content with reduced latency & high transfer speed via 275+ global points of presence (PoPs). This makes VdoCipher one of the best Secure Video CDN providers.
You can upload your video content and reuse the CDN-based encrypted version of your video through many modes. Even integrations are supported by a web interface as well as via API for technical and bulk usage. Also, your processed videos will automatically have adaptive bitrate streaming for different bandwidth support.
Note: DRM encryption for Videos is currently the best available technology to safeguard your videos from piracy. This technology is encouraged by both Apple & Google.
CloudFront
Amazon CloudFront is a Content Delivery Network managed by Amazon Web Services. The Amazon CloudFront offers multiple offers for media streaming, both live events and pre-recorded media files. For on-demand streaming, one can use multi-bitrate adaptive streaming in HDS, HLS, MPEG-DASH formats.
CloudFront is easy to use for video production with AWS Media Services like AWS Elemental MediaConvert and AWS Elemental MediaPackage. For Live streaming, CloudFront is optimized to handle high request volumes with ultra-low latency streams. AWS CloudFront uses a low latency origin server, AWS Elemental MediaStore, for live streaming. AWS Elemental MediaLive and AWS Elemental MediaConnect for video encoding and transcoding.
Cloudflare
Cloudflare CDN delivers high-quality video content across the globe with shorter video startup times and reduced buffering. Cloudflare’s CDN spans over 100 countries covering over 250 cities. For videos, Cloudfare offers performance and security services with SSL / TLS 1.3 Encryption, Cache Configuration, high-quality HTTP streaming, Live broadcast using Stream Player or any HLS/DASH player such as Shaka player. Other key features include Bandwidth Alliance partnerships to lower or eliminate data egress costs, Adaptive Bitrate (ABR) encoded video support, Integrated WAF and rate-limiting.
Tata Communications – Bitgravity
In 2011, Tata Communications acquired US-based Content Delivery Network provider, BitGravity. The acquisition of BitGravity, the first CDN to offer video on demand and live streams on the internet, enhanced Tata Communications global CDN offering. In 2008, Tata Communications invested $11.5 million in BitGravity and bagged clients like NDTV, Quick Heal and more. Tata Communications CDN supports Content Ingestion, Adaptive Bitrate, Video Transcoding, Transmuxing and video content distribution. Their Video CDN service delivers high-quality videos with fast start-up and reduced buffering across multiple devices.
Azure-Akamai
In 2019, Akamai integrated Akamai’s content delivery network (CDN) capabilities with Microsoft Azure Media Services and Blob Storage. For media organizations, the integration makes cloud-based video processing to playback easy and cost-effective. Through Azure Media Services, Akamai enhances the delivery of on-demand and live streaming with lower latencies and more media workflow integration choices. Microsoft Azure, Azure Media Services and Azure Storage with Akamai’s Edge mitigate the cost and maximize performance for content providers.
Verizon CDN (Edgecast)
Following the acquisition of Yahoo!/Verizon Media by Apollo Global, Verizon’s serverless and Content Delivery Network (CDN) services, has been rebranded as Edgecast. Edgecast offers CDN, streaming delivery services, Edge computing and serverless computing.
Coming to Verizon Web Acceleration, the content delivery network (CDN) offers high-quality performance for web and mobile apps. Using advanced caching techniques and over 165 PoPs, Verizon CDN reduces latency and maximizes web speed. Having stringent security and massive capacity, Verizon’s CDN solution is ideal for high traffic applications. It includes E-commerce, video stream optimization, live video streaming, online banking and more. Further, the intelligent load balancing and compression speed up secure content delivery even in the remotest locations.
Limelight Networks CDN
Arizona-based CDN provider Limelight Networks offers fast and secure delivery of video streams and other digital content. Limelight has nearly 135 global POPs and direct connections to 1000+ ISPs. Its on-demand and live video delivery services with advanced video delivery serve video at high-quality with the lowest buffer. Limelight cloud-based, end-to-end workflow includes automatic transcoding and transmuxing at multiple formats. Limelight’s online video platform is fully integrated with CDN. It lets you efficiently manage and serve video content without the need for custom coding or separate CDN integration. Limelight’s clients include FOX, Marvel, BBC, Nintendo and more.
Fastly
Edge cloud platform Fastly comes with real-time observability, programmatic control, streamlined workflows, built-in security and more. Fastly CDN is improving the user experience with decreased web and application load time. Fastly’s Streaming Media Delivery offers broadcast-quality VOD and live experience on any device with 145+ Tbps capacity.
Fastly supports all major HTTP video streaming formats with easy API integrations. Fastly’s modern CDN caches and rapidly delivers long-tail, on-demand videos. Fastly’s Origin Connect offers dedicated bandwidth for large spikes in live streaming videos. Latency gets reduced by sending traffic across secure private paths instead of over public internet. Other key features include Time to Live (TTL) controls, Edge logic and advanced content delivery control, Real-time log streaming, Always-on DDoS mitigation, Content compression and more.
Telco CDN
The exponential growth in Over-the-Top (OTT) streaming services has opened ways for mobile operators and communications service providers (CSPs) to gain revenues and subscribers. To do so, telecommunications service providers (TSPs) have started to launch their own CDNs. As they own the network over which content gets transferred, Telco CDNs have advantages over traditional CDNs. The data reaches the end-user more securely and quickly due to being cached deep in the providers’ network. Providers also get better control over their resources and cost advantage by having their own CDN. In India, Reliance Jio and Airtel have their own CDNs. Jio and Cisco have partnered for mobile CDN integration while Airtel is leveraging Limelight Networks CDN. Content providers with packages on quality of service (QoS) will emerge as the winner.
FAQs
What is CDN video streaming?
Content Delivery Network (CDN) to deliver video content more efficiently by distributing video segments across multiple servers worldwide. This reduces buffering and latency by bringing content closer to viewers and helps avoid overloading the origin server. CDNs cache video files or segments, allowing quicker delivery, whether for on-demand or live streaming. This improves playback quality, reduces load times, and prevents bandwidth issues.
How do e-Learning platforms benefit from Video CDN?
Online courses are full of static content like images, audio and video clips. Caching via CDN serves the purpose to serve online learning platforms faster and securely to learners from different locations. Other benefits include enhanced user experience, fast loading time, content availability even at excessive traffic or server outages. Deploying CDN also addresses data security and privacy concerns.
Do VOD, OTT and other media platforms use Video CDN?
For them using Video CDN is a must otherwise the latency will become too long and will also start blocking their main server. This also satisfies their purpose of serving a smooth user experience, fast loading time and video content availability even at aggressive traffic. Most OTT platform and other VOD platforms use secure video hosting services like VdoCipher to protect their original content from piracy as it is their most important data asset.
What is meant by Cache Miss and Cache Hit?
A cache miss is an instance when something gets searched up in the cache, and the data isn’t found. This happens when a request is made to the CDN for the first time. In case of a cache hit, the cache successfully serves the content or request.
What does Time-to-Live (TTL) refer to in respect to Content Delivery Network?
Time-to-Live refers to how long a cached content is served from the CDN edge server before a new copy gets fetched from the origin server. In other words, TTL controls the refresh rate of the cache copies stored on the CDN.
Does CDN affect a website’s SEO?
CDNs affect the SEO of a page and significantly improve the search ranking. CDN provides faster load time, image and session optimization, reduced latency, caching algorithms, and canonical headers to boost SEO.
References:
- What is a CDN? – Content Delivery Network Explained – AWS – link
- The State of CDNs Today and What AI‐Assisted CDN Means for the Future – link
- AWS Innovator: Netflix | Case Studies, Videos and Customer Stories – link
- How the Cloud and CDN Architecture Works for Netflix – link
Ensure Smooth Video Streaming Regardless Of Geographic Locations
With AWS-powered servers, Video DRM & CloudFront CDN infrastructure Vdocipher ensures video piracy protection with smooth video playback across 6 continents. Such an infrastructure can securely deliver your video content with reduced latency & high transfer speed via 275+ global points of presence (PoPs). This makes VdoCipher one of the best Secure Video CDN providers.


My expertise focuses on DRM encryption, CDN technologies, and streamlining marketing campaigns to drive engagement and growth. At VdoCipher, I’ve significantly enhanced digital experiences and contributed to in-depth technical discussions in the eLearning, Media, and Security sectors, showcasing a commitment to innovation and excellence in the digital landscape.