One of the first step to executing an E-Learning video production is to select a suitable camera. With the multitude of cameras available in the market and the diverse range of features they offer, it is very easy to get confused. In this blog I explore various features and functionalities that different kinds of cameras offer. In this analysis I discuss DSLRs, Camcorders, WebCams and Digital Cameras. Each of these cameras come at different prices, and whether they are right for you depends on what features and functionalities you are looking for. I’ll begin with a discussion of the technical concepts necessary to understand the specs that cameras offer. An understanding of these concepts will help you navigate much of the jargon that goes around regarding cameras for E-Learning Video Production.
Price of the camera often becomes the driving filter when selecting a camera for E-Learning video production. Along with the camera type I have added the price range to expect for the camera.
Camera Features
- Lens Quality
- Light Sensitivity of Image Sensor
- Aperture Size
- Camera Shutter Speed
- Size of Image Sensor
- Resolution
- Depth of Field
- Autofocus
- Monitor Screen
- Frames Per Second
Different Cameras
10 features in a camera for E-Learning Video Production
Quality of image is determined by:
1. Lens Quality
There are three qualities of lenses to consider: Range of focal Length, Material (Glass/Plastic), and angle of capture and Optical Zoom.
Optical Zoom is defined, for cameras with variable focal lengths as the ratio of maximum focal length to the minimum focal length. Basically a high focal length corresponds to higher magnification and narrower angle of view, whereas low focal length is used by wide angle lenses at lower magnifications. Wide Angle Lens have a range between 35 to 24mm focal length, covering angular range of between 64 Degree to 84 Degree.
What kind of focal length to use for your E-Learning Video Production depends on the camera positioning. If your camera is placed at the opposite end of a big classroom you would need a large focal length lens – high optical zoom cameras would come in handy here. On the other hand if the camera is placed close to the teacher, then a wide-angle lens with low focal length is appropriate, to take in the entirety of the blackboard. High optical zoom gives you much more options about where to place the camera to get the desired look.
Wide angle lenses tend to magnify the distance between the foreground and the background. This is not very desirable for E-Learning Videos. For this reason it is recommended that you record your E-Learning videos at high optical zoom.
It is important to note that digital zoom is different from optical zoom, and in fact only causes blurring of the video in exchange for a narrower final image.
2. Light Sensitivity of Image Sensor –
The light entering through the lens and the aperture is captured and processed by the image sensor. ISO is a measure of how sensitive the image sensor is to the incoming light. A high ISO number means high sensitivity, meaning that a low exposure time is required for shooting the picture. A high ISO is not always desirable, as it adds noise to the image.
ISO numbers range from 64 to 12800 (with multiples of 2 beginning from 100, as in 100, 200, 400…) A light sensor with ISO 400 has twice the light sensitivity of ISO 200. Along with the aperture size and camera shutter speed, light sensitivity determines that a photo is properly exposed.
3. Aperture Size
Light enters the sensor through the aperture. The greater the aperture size the more light is allowed. High ISO sensors can work with small aperture sizes as well. The f-number is a ratio of the focal length to the aperture size – the lower the f-number the higher the aperture size.
4. Camera Shutter Speed
The camera shutter speed determines the time of exposure of the image sensor. A greater shutter speed means less exposure of sensor to light. High ISO sensors can work with faster shutter speeds.
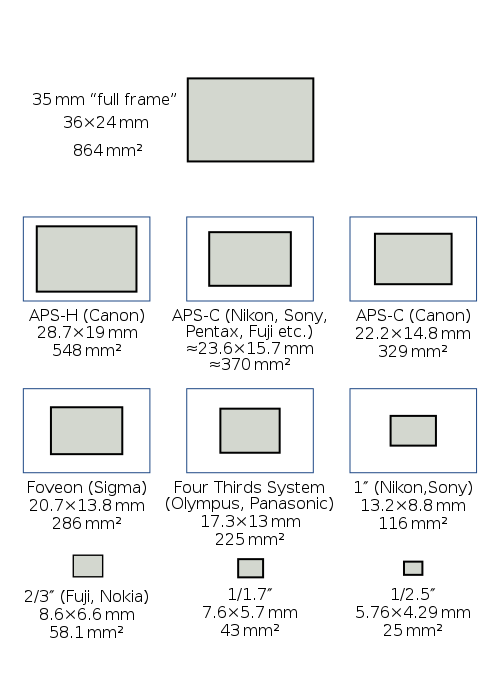
5. Size of Image Sensor
The size of the image sensor determines how much light is used to form an image. Full Frame Image Sensor size is 35mm, and is used in high-end DSLRs. A higher image sensor requires a high focal length lens, making the camera + lens setup bulky. Most DSLRs and high-end digital cameras use the APS sensor size, in which the size of the image sensor is around 24 X 18mm. APS is less than half the size of the 35mm image sensor, for which reason it is cheaper to manufacture, and considerably less bulky. Most smartphone cameras on the other hand have much smaller image sensors. Along with the Megapixel resolution, the image sensor size determines the quality of images.
6. Resolution
This Number of pixels that the image sensor captures. For point and shoot smartphone cameras the number of megapixels is marketed as the most important aspect of the camera required to produce a quality image. However, if the image sensor is small, then higher resolutions means that the image is very noisy.
7. Depth of field
This is the depth of the object that the camera can capture clearly. A shallow Depth of Field means that the subject is in high focus, and stands out from the background. High Depth of Field on the other hand means that a large area of the image is in focus, and for this reason it is great for landscape shooting. is directly proportional to the distance of camera from object. DOF is inversely proportional to size of aperture. DOF is inversely proportional to focal length. For E-Learning videos a shallow depth of field is desirable.
8. Autofocus
This is the number of points on the viewfinder of the camera that the camera can focus on. The more the number of autofocus points the better is the ability of the camera to focus on a desired object to get an image.
Read more on Autofocus here: https://photographylife.com/dslr-autofocus-modes-explained
9. Monitor Screen
Although a secondary feature, a large monitor screen helps you get a better sense of the video being taken, allowing you to edit settings in real time to get the desired image.
10. Frames Per Second
FPS is the number of frames included in one second of video. Basically, the maths works as follows:
- The greater the framerate the more continuous does the video feel, and therefore a better resolution is achieved
- Greater framerate means greater video file size, causing demands on bandwidth
- Framerate works ideally when the screen refresh rate is proportional to video frame rate. US and Canada receive 60Hz power supply. For this reason 30FPS is naturally better for video streaming in these countries. In Europe, India and much of the rest of the world power frequency is 50Hz, for which reason 25fps is ideal in these countries.
Different FPS
- 15fps – This was the frame rate used by early films
- 24fps – This is the framerate used by the movie industry. This number was a compromise to strike a balance between minimizing cost of using film while retaining the continuity necessary for the video.
- 25fps – European and Indian video – It is possible to convert 30fps video to 25fps video
- 30fps – still some jerky motion, but mostly optimal
- 60fps – very little jerkiness, but higher frames per second means greater video file size, requiring greater bandwidth
A frame rate in the range of 25-30 fps is optimal for E-Learning video productions, ensuring the quality of video and also not causing the file size to be too big.
Further reading – Video Frame Rates, Steve’s Digicam
Cameras for E-Learning Video Production
DSLRs – Price Range $400-500
Digital Single-Reflex Cameras use a combination of mirrors and lenses to shoot high quality photos and videos. Along with the highest range of quality features, DSLR offers a great ability to control the image. To get the best results for your E-Learning video production from a DSLR, you really need know your camera so that you can control individual settings manually.
An important thing to note is that videos are shot on DSLRs in the RAW format. This makes them very big in size – for example you will need a 32GB card to just shoot 15 minutes of video.
Image sensor in a DSLR is bigger than in point and shoot cameras or camcorders – meaning that even if a camcorder and a DSLR have the same number of megapixels, there would still be a great deal of noise in the camcorder. This is because in smaller sensor the adjacent pixels can communicate, causing noise.
With DSLR you have much greater options to change the depth of field as per your wishes
For E-Learning videos a shallow depth of field is desirable, as the main focus is on the speaker and the blackboard/ whiteboard.
Among lenses, the 70-200mm lens is one of the most popular DSLR lenses. Wide angle lens (24-35mm) are on the other hand used for landscape photography. To cover entire width of the whiteboard from a short distance it may be more desirable.
Most Popular DSLRs
Nikon D5200 24.1MP Digital SLR Camera (Black) – $510
- This camera boasts an ISO range from ISO 100 to ISO 6400
- 18-55mm and 18-140mm lens are available with this DSLR
- 24.1 MP optical sensor resolution
Canon EOS 700D 18MP Digital SLR Camera (Black) – $390
- Optical Sensor Resolution – 18MP
- CMOS Optical Sensor Technology
- 9-point AutoFocus system
Camcorders – Price Range – $150-200
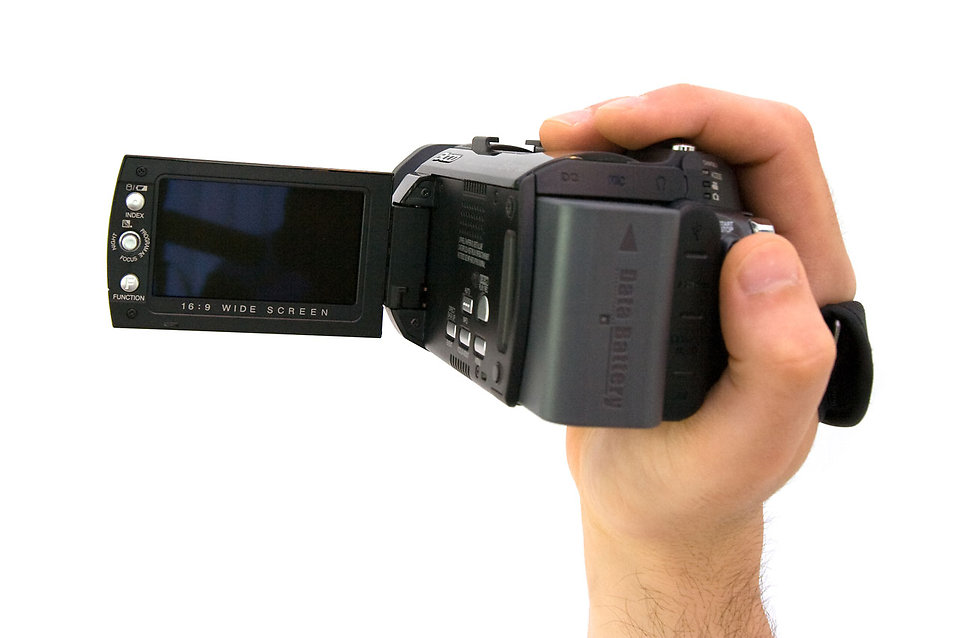

Camcorders are designed specifically for video shooting. Most camcorders support containers such as MPEG-4 and the codec H.264, meaning that you do not need to spend time and computing power encoding the video to a usable format. Sony uses the XAVC format, which supports the H.264 codec. Video editing is a very processor-intensive process, and shooting on a camcorder makes the video editing much more convenient. Some of the key qualities of a good camcorder are:
- Zoom Lenses – for example optical zooms of 30X can be expected from good camcorders. Glass lens have much better quality than plastic lens.
- Image stabilization – Because they are designed for video shooting, the processor and lens system can be designed to enhance image stabilization. Additionally face detection features can be incorporated in the software for the camera, enabling ability to better focus the camera. Optical Image Stabilization is better as lenses adjust to movements to steady the image, whereas Electronic Image Stabilization uses algorithms that may degrade picture quality.
- CMOS Sensors – Most camcorders currently use the CMOS sensor. For example Canon uses EXMOR R sensor, which is about half the size of the APS-C used in DSLRs. The image sensors used by camcorders are much bigger than sensors in the camera phones.
A useful guide to all camcorder features can be found on Lifewire
Some of the most popular camcorders are:
Sony HD Video Recording HDRCX405 Handycam Camcorder
- 30X Optical Zoom
- 26.88mm wide angle lens
- Uses Sony’s XAVC video format supporting H.264 codec
- Maximum Bitrate: 50Mbps, Frame Rate: 60p
- Image stabilization
- Exmor CMOS sensor
Panasonic HC-VX981K Ultra HD Camcorder with Wi-Fi Twin Camera and 4K Photo Features (Black)
- 20X Optical Zoom
- Leica Decoma Lens
- 5-axis Hybrid Optical Image Stabilization
- 4K Shooting
WebCams – $60-100
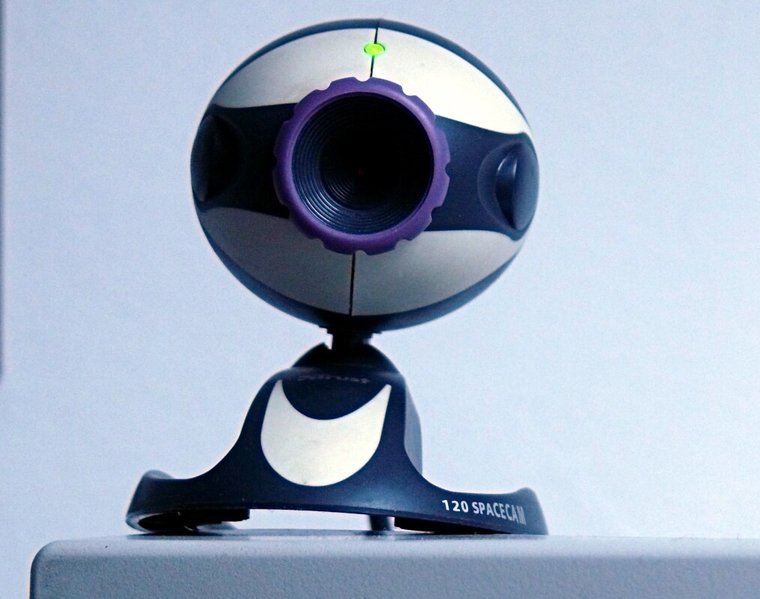

Webcams are a cheap option, and besides being of use for your E-Learning video production, can also be used for conference calls. Some selling points of webcams include a high megapixel resolution, Auto Focus, glass lens, ability to control brightness exposure, and face tracking.
Lifewire has a good guide on webcam features to look out for.
Microsoft Q2F-00013 USB 2.0 LifeCam Webcam
- 1080p HD sensor
- Glass element lens
- Auto focus
- Wide angle lens
Logitech C920 HD Pro Webcam (Black)
- 1080p HD sensor
- Glass element lens
- H.264 video compression
- Face tracking and motion detection using logitech software for windows
Digital Cameras – $80-100
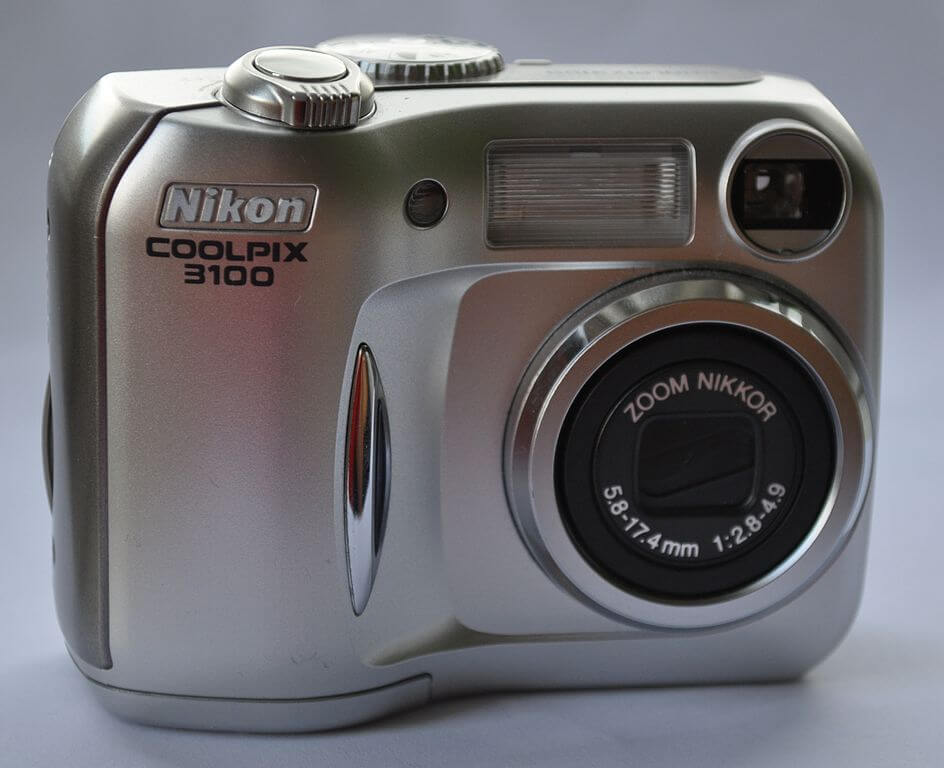

Digital cameras are, along with webcams, the cheapest option for your E-Learning video production. Good high-end digital cameras such as Nikon Coolpix have image sensors much bigger than those of lower end cameras, and are almost comparable to camcorders. In comparison to camcorders, digital cameras may have a smaller range of optical zoom, meaning that your options regarding camera placement for your E-Learning video production are quite limited. On the other hand the image quality, given an optimal camera placement, is comparable to camcorders. When working on a budget, a quality digital camera is a good idea given that you have an understanding of its limitations.
Recommended Cameras:
Sony DSCW800/B 20.1 MP Digital Camera (Black)
Nikon Coolpix S2800 20.1 MP Digital Camera
FAQs
What is the hand camera price?
There is no definitive answer to this question as the price of a hand camera can vary greatly depending on the make and model of the camera, as well as the specific features and accessories that are included. However, generally, hand camera pricing starts at around $50 and goes up to $500.
What are some of the basic features to look for while selecting a camera for video production?
High Definition (HD) recording- This will ensure that your videos look sharp and clear.
Autofocus- This will help to keep your subject in focus, even if they are moving around.
Image stabilization- This will help to reduce any camera shake, making your videos look smoother.
Low light performance- This will allow you to shoot in dimly lit conditions, without compromising on quality.
What are the most common hand camera requirements for E-Learning Video Production?
The most important factor is the capability of the camera to capture high-quality video and audio. Many cameras nowadays are able to do this, so it is not as big of a concern as it once was. Another important factor is that the camera should be easy to use with a user-friendly interface.
Supercharge Your Business with Videos
At VdoCipher we maintain the strongest content protection for videos. We also deliver the best viewer experience with brand friendly customisations. We'd love to hear from you, and help boost your video streaming business.



Leave a Reply